INSPECTION AND REPLACEMENT OF WATER-COOLED SYSTEMS FOR INDUSTRIAL GENERATORS
Industrial generators, especially those operating continuously and at high capacity, must be maintained to ensure stable and safe performance. One of the most critical factors in achieving this is the cooling system—the silent heart that prevents engine overheating. Among current cooling technologies, water-cooling systems are widely used in industrial generators due to their efficient heat transfer capabilities. This article provides a comprehensive overview of their structure, working principles, the role of coolant, and proper inspection and replacement procedures.
.jpg)
1. Overview of the Water-Cooling System in Generators
1.1. Basic Function
When a generator operates, the internal combustion engine produces significant heat due to fuel combustion and friction between engine components. Without timely cooling, excessive temperatures can cause material expansion, component deformation, or even engine failure. The water-cooling system operates on a circulation principle, transferring heat from the engine's hot surfaces to the air via coolant fluid.
1.2. Main Components
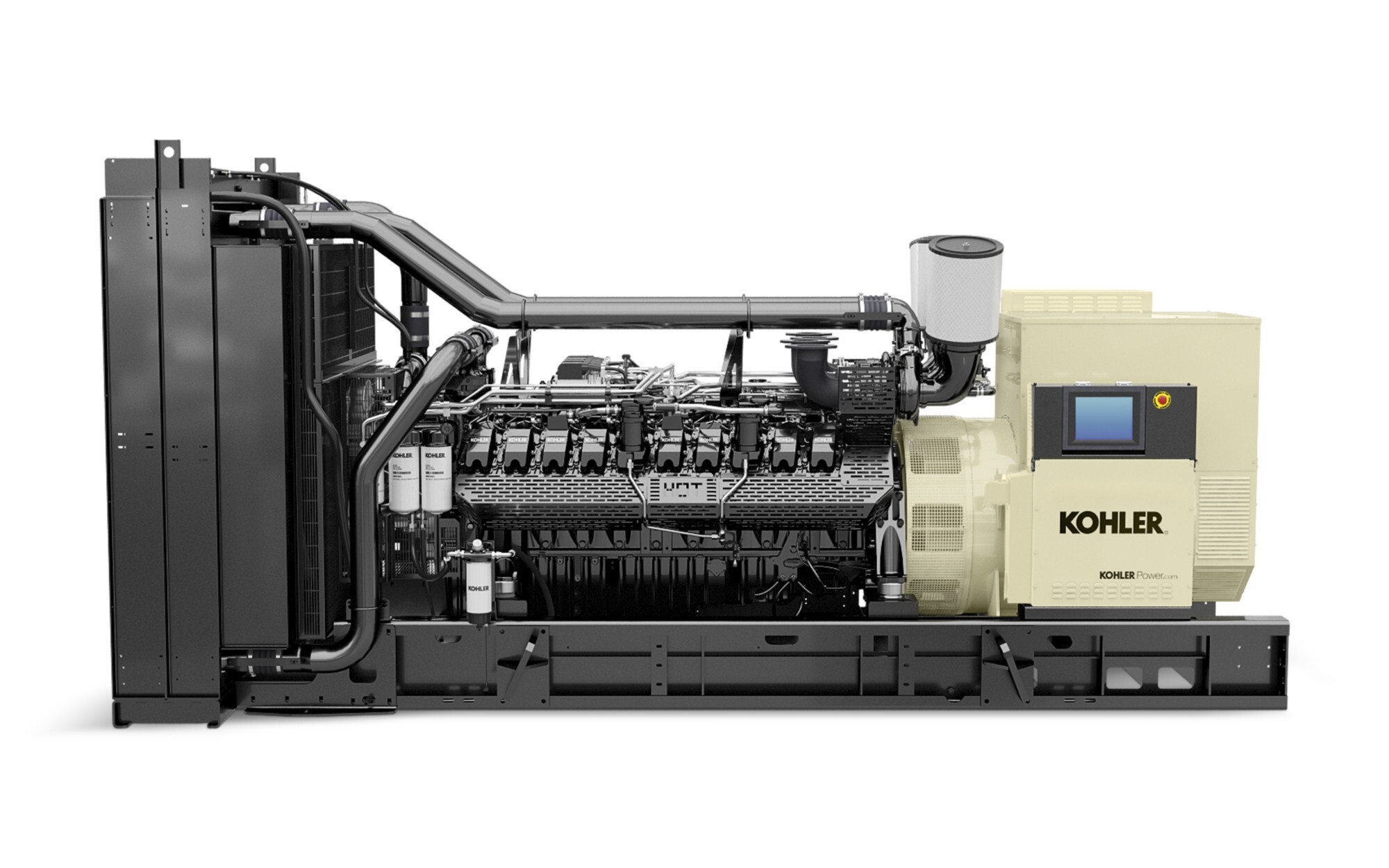
A typical water-cooling system includes:
-
Engine Block: The primary heat source, designed with water passages around cylinders and cylinder heads to conduct heat outward.
-
Water Pump: A centrifugal pump that circulates coolant throughout the system.
-
Thermostat: A thermal valve that regulates coolant flow, allowing circulation through the radiator only when the operating temperature (~85°C) is reached.
-
Radiator: A heat exchanger where hot coolant releases heat to the air and cools down, assisted by airflow.
-
Cooling Fan: Enhances airflow across the radiator to improve heat dissipation, especially during stationary operation.
-
Expansion Tank: Absorbs expanded coolant at high temperatures and returns it when cooled, preventing pressure overload.
-
Piping System: Delivers coolant across all components in a closed-loop cycle.
2. Understanding Coolant
.jpg)
2.1. What Is Coolant?
Many believe regular water suffices for cooling. In fact, specialized coolant is a synthetic solution containing:
-
Glycol (Ethylene or Propylene Glycol): Prevents freezing in cold weather and boiling at high temperatures.
-
Corrosion and Rust Inhibitors: Protect metal surfaces from chemical and electrochemical damage.
-
pH Stabilizers and Anti-scaling Agents: Prevent limescale and deposit build-up in the piping.
-
Color Dyes: Distinguish coolant types and detect leaks.
-
Distilled or Deionized Water: Ensures purity, avoiding scaling from mineral content.
2.2. The Role of Coolant
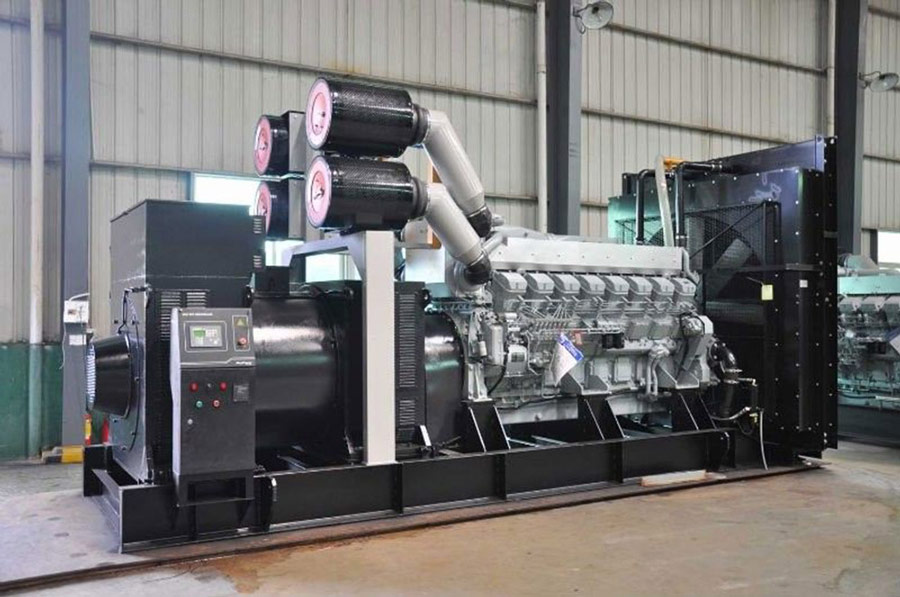

Coolant performs several essential functions:
-
Heat Dissipation: Absorbs and transfers heat from the engine to the radiator.
-
Thermal Regulation: Helps the engine reach and maintain optimal operating temperature.
-
Mechanical Protection: Prevents overheating, deformation, piston seizing, or cylinder wear.
-
Freeze and Boil Protection: Ensures stability in all weather conditions.
-
Internal Corrosion Protection: Extends the lifespan of radiators, pumps, pipes, and engine components.
3. When to Inspect and Replace Coolant?

Coolant degrades over time—its chemical properties break down and can become harmful if not replaced.
-
First replacement: After 250 hours of operation or the first 12 months.
-
Subsequent replacements: Every 1,000 operating hours or every 2 years, whichever comes first.
-
Routine inspection: Weekly coolant level checks are recommended. Refill as needed.
-
Coolant quality check: If the color turns cloudy, reddish-brown (rust), or shows suspended particles—replace immediately.
Note: Degraded coolant can become acidic, accelerating corrosion and system damage.
4. Signs of Cooling System Issues
Early detection of faults helps prevent severe damage:
-
Unusually high engine temperature: Temperature gauge exceeds safe limits.
-
Coolant system warning light: On advanced generator models.
-
Visible leaks: Coolant spots (green, red, or orange) near the radiator or hoses.
-
Coolant discoloration or unusual smell: Sweet or burnt odors (burning glycol), potentially with white exhaust smoke.
-
Unusual noises from the pump or fan: Possible due to pump failure, impeller wear, or stuck bearings.
5. Correct Coolant Inspection & Replacement Procedure
5.1. Periodic Inspection Steps
-
Coolant level: Check the “MIN – MAX” marks on the expansion tank when the engine is cold.
-
Coolant clarity: Visually compare with new coolant.
-
Leak detection: Inspect joints, clamps, radiator body, and water pump.
-
Hose condition: Check for swelling, cracks, soft spots, or brittleness.
5.2. Coolant Replacement Procedure
Step 1: Drain Old Coolant
-
Let engine cool completely.
-
Slowly open the radiator cap.
-
Open drain valves on the radiator and engine block (if available) and collect the coolant.
Step 2: System Flushing (Recommended)
-
Close the drain valves.
-
Fill with clean water or specialized flushing solution.
-
Run the engine for 15–20 minutes.
-
Let cool and drain again.
Step 3: Add New Coolant
-
Choose high-quality coolant (e.g., Glysantin, Donaldson, MTU, or Gly Coolant).
-
Slowly fill into the radiator.
-
Start engine, monitor coolant level, and bleed air as needed.
-
Seal the radiator cap after stabilization.
Step 4: Post-Replacement Monitoring
-
Check for leaks.
-
Monitor operating temperature during initial cycles.
-
Recheck coolant level after a few hours or the next day.
6. Which Coolant Is Best for Industrial Generators?
For critical equipment like industrial generators—where continuous, stable operation is essential—choosing the right coolant is crucial. Among various options on the market, GLY COOLANT®, manufactured by BASF – Germany, stands out for its high performance and reliability in large-capacity industrial engines.
.jpg)
Key Features of GLY COOLANT®:
Advanced Corrosion Protection with OAT Technology
.png)
Utilizes Organic Acid Technology (OAT), forming a micro-thin protective layer on metal surfaces. This prevents oxidation and corrosion, protecting aluminum radiators, pipes, water pumps, and cast iron/steel engine blocks—reducing wear and extending component life.
Excellent Freeze and Boil Protection
.png)
With high-purity ethylene glycol, GLY COOLANT® achieves a freezing point down to -38°C and boiling point up to ≥108°C (depending on mix ratio), ideal for outdoor or extreme operating environments.
Superior Anti-Scaling Performance
Pre-mixed and ready to use, GLY COOLANT® ensures consistent concentration and convenience for maintenance teams. Deionized water in its formula eliminates scaling risks commonly associated with tap water.
Anti-Foaming Additives

Minimizes foaming in high-pressure systems—critical for heat transfer efficiency and uniform coolant circulation, preventing surface erosion and maintaining thermal balance.
Free from Harmful Substances
.png)
Formulated without phosphates, nitrites, amines, silicates, or borates, which can cause deposits or adverse reactions with metals. This keeps the cooling system clean and functional over time.
International Standards Compliance

Certified to rigorous standards including ASTM D3306, ASTM D1384, DIN 51 757-4, ensuring safety and efficiency in demanding industrial environments. Compatible with recommendations from major engine manufacturers.
Conclusion
The cooling system is your generator engine’s first line of defense against heat-related damage. Understanding its components, operation, and proper maintenance—especially coolant inspection and replacement—is vital to enhancing performance, minimizing repair costs, and extending equipment lifespan. Make cooling system care a routine part of your generator maintenance schedule.
Viet Duc Joint Stock Company
Address: 274 Ngo Quyen Street, Van My Ward, Ngo Quyen District, Hai Phong City
Phone: 02253.765.721 Fax: 02253.752.450
Email: sales@vietducjsc.vn
Website: www.vietducjsc.vn
Hotline 1: 0989.080.608 Hotline 2: 0904.085.608








